COMP3056 Computer Vision 2 -- SIFT
Table of Contents
- Point Features: SIFT
Point Features: SIFT
Feature Descriptor: Feature Vectors that describes sections of an
image
Purpose of SIFT: Create a good feature
detection/description algorithm that is invariant to scale, translation,
rotation and illumination changes
Scale Invariant Feature
Transform (SIFT): Transform image data into scale-invariant
coordinates relative to local features
[IMPORTANT] SIFT Overview
1-2 Sentences per step enough
- Scale-space extrema detection - For Scale Invariance
- Search over all scales and image locations
- Detect points that are invariant to scale and orientation
- Keypoint localization - For Translation Invariance
- A model is fit to determine the location and scale
- Keypoints are selected based on measures of their stability
- Orientation assignment - For Rotation/Orientation Invariance
- Compute best orientation for each keypoint region
- Keypoint descriptor - For Illumination Invariance
- Use local image gradients at selected scale and rotation to describe each keypoint region
[UNDERSTAND] Detailed Steps
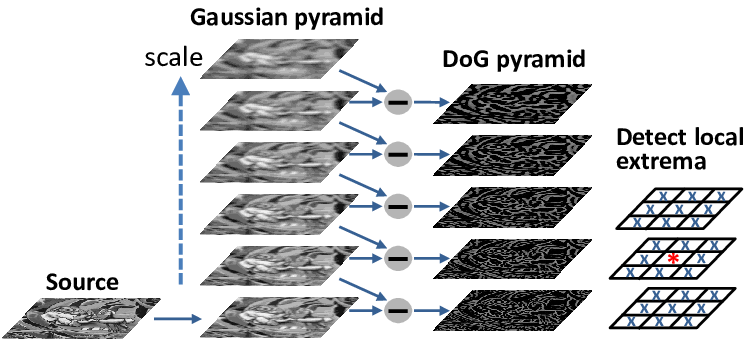
Step 1: Scale-space extrema detection - Scale Invariant
Get rid of some details while not introducing new false details - Using Gaussian Blur
- Generate scale space octaves of the original image
- Each octave's image size is half of the previous one
- Within an octave, images are progressively blurred using the Gaussian Blur operator
Step 2: Keypoint localization - Translation Invariant
Get rid of low contrast keypoints or keypoints lied along an
edge - Comparing DoG value with the preset threshold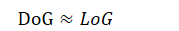
- Produce DoGs using two consecutive images in an octave for all octaves
- Detect the maxima/minima in the DoG images (The greatest or least one of all neighbors, 8 surrounding pixels, 9 upper pixels, and 9 lower pixels)
- Reject the keypoints if they had a low contrast or if they were located on an edge
Step 3: Orientation assignment - Orientation/Rotation Invariant
Figure out the most prominent orientation in the region and assign it to the keypoint - Calculating gradient magnitude and direction of the region around the key point
- To assign an orientation we calculate the gradient magnitude and direction of a small region around the keypoint
- Using the histogram, the most prominent gradient orientation is
identified
- Peak of the histogram
- Assign it to the keypoint
Step 4: SIFT Descriptor - Illumination Invariant
Compute a descriptor for the local image region(window) around each keypoint
- Region normalization
- Rotate the window to standard orientation
- Scale the window size based on the scale at which the point was found
Full version:
- Divide the 16x16 window into a 4x4 grid of cells
- Within the 4x4 cell, the orientations and gradient magnitudes are calculated
- Put these orientations into an 8 bin histogram (the amount added to the bin depends on the magnitude of the gradient)
- 16 cells * 8 orientations = 128 dimensional descriptor
- Normalize the vector
- Clamp all vector values > 0.2 to 0.2
- Renormalize
[IMPORTANT] Properties
- Invariance
- To be robust to intensity value changes
- Use gradient orientations
- To be scale invariant
- Estimate the scale using scale-space extrema detection
- Calculate the gradient after Gaussian smoothing with this scale
- To be orientation invariant
- Rotate the gradient orientations using the dominant orientation in a neighborhood
- To be illumination invariant
- Working in gradient space, so robust to I = I + bbNormalize vector to [0..1], robust to I = αl brightness changes
- Clamp all Vector values > 0.2 to 0.2, robust to "non-linear illumination effects"
- To be robust to intensity value changes
(No need to remember the specific number like 0.2, just remember the idea)
- Fast and efficient
- Can run in real time
- Lots of code available
- Can handle
- Changes in viewpoint, up to about 60°out of plane rotation
- Significant changes in illumination, sometimes even day vs. night
[UNDERSTAND] Uses / Applications
- Pose estimation
- 3D reconstruction
- Object recognition
- Image retrieval
COMP3056 Computer Vision 2 -- SIFT
https://jerry20000730.github.io/wiki/Lecture Note/COMP3065 Computer Vision/CV3/