COMP3056 Computer Vision 1 -- Image Regions and Patches
Table of Contents
Segments and Patches
Segments is irregular, or rectangular
Patches always rectangular
Usage of Segments and Patches
- Track objects
- use different views to reconstruct 3D
- detect object classes and recognize specific objects using pre-stored model
Features and Feature Vector
Feature is a piece of information about the content
of an image
Feature vector refers to a vector that
contains the concatenation of multiple features in an image.
Classification of Features
- Color Features
- Texture Features
- Local Binary Patterns (LBP)
- For each center pixel \(p_c\),
create an 8-bit number \(\{b_1, b_2, b_3,
b_4,b_5, b_6, b_7, b_8\}\), for \(i \in
[1, 8]\), the local binary pattern will be: $$b_i = \left\{\begin{array}{rcl}0 & & (p_i \leq p_c)\\1 & & (p_i \gt p_c)\end{array}\right.$$
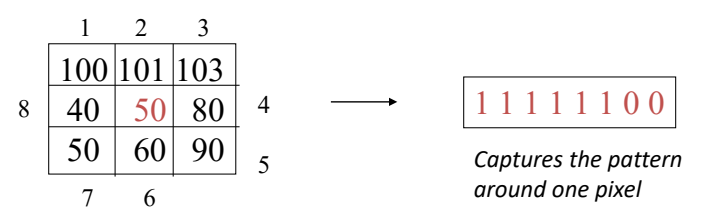
- For each center pixel \(p_c\),
create an 8-bit number \(\{b_1, b_2, b_3,
b_4,b_5, b_6, b_7, b_8\}\), for \(i \in
[1, 8]\), the local binary pattern will be: $$b_i = \left\{\begin{array}{rcl}0 & & (p_i \leq p_c)\\1 & & (p_i \gt p_c)\end{array}\right.$$
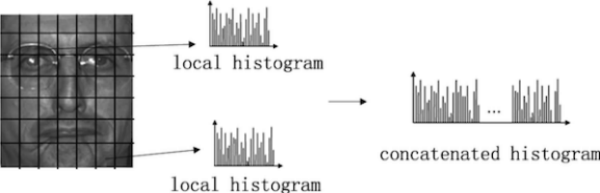
- LBP Feature Vector
- Divide the patch into cells e.g. 16 x 16 pixels per cell
- Compute local path description number of each pixel
- Histogram these numbers over each cell
- 将上面的八位二进制转成十进制
- 所以ppt上说256-d dimension
- Normalize each histogram (optional)
- Concatenate histograms to make the feature vector
- Local Binary Patterns (LBP)
- Shape Features
- focus on image gradient measures
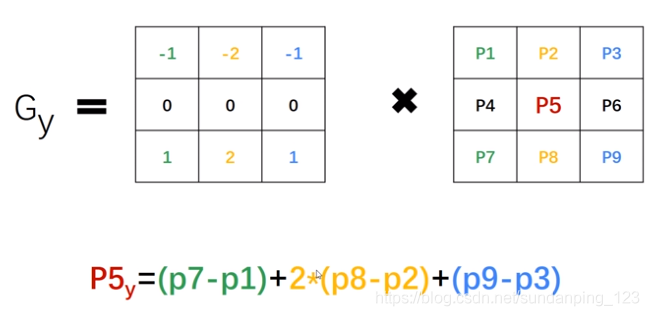
Image Derivative (只需要理解sobel filter)
Definition of Sobel Filter: 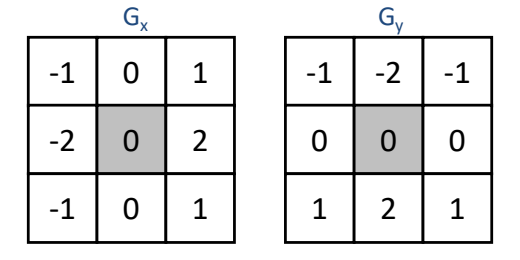 The
calculation process for Sobel Filter:
The
calculation process for Sobel Filter: 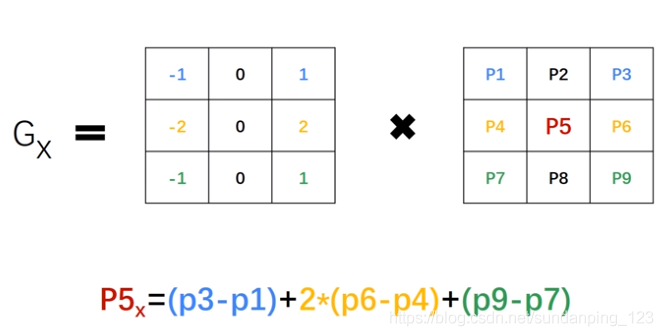
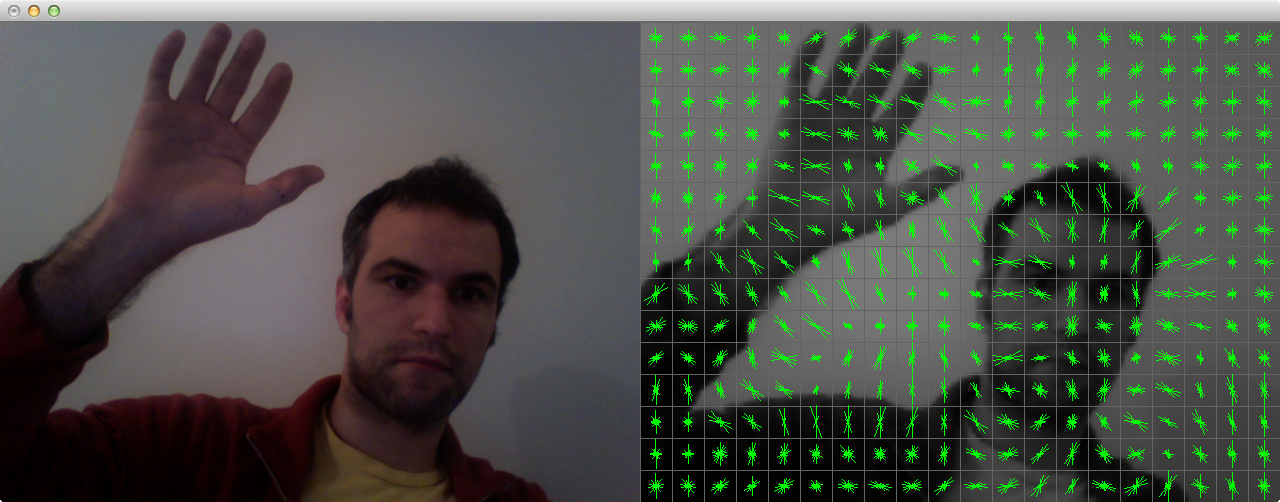
[IMPORTANT] Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HoG)
The steps of HoG
- Divide the patch into small cells

- Define slightly larger blocks, covering several cells

- Compute gradient magnitude and orientation at each pixel
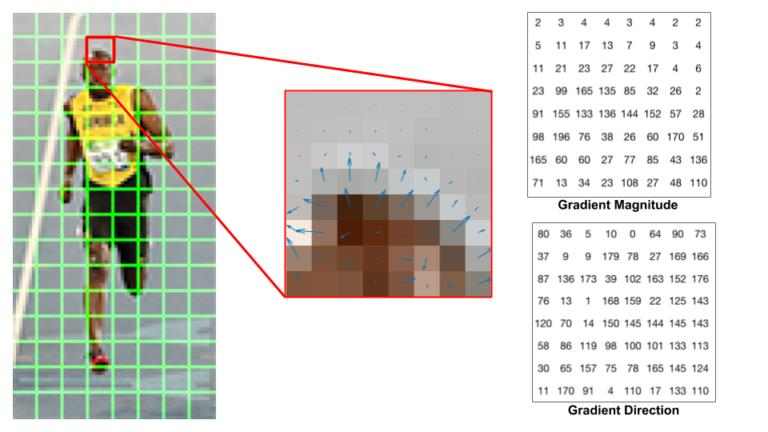
- Compute a local weighted histogram of gradient orientations for each cell, weighting by some function of magnitude.
- The histogram is a vector of 9 bins corresponding to angles 0, 20, 40, 60 … 160
- A bin is selected based on the direction(角度), and
the vote (the value that goes into the bin) is selected based on the
magnitude
- 先根据角度算每个格子的占比,下图中左红色圈代表角度为10度,介于0-20度之间,10
= 0 * 0.5 + 20 * 0.5,知道这个占比之后按照占比将右边圈代表梯度大小,则0
bin里是4 * 0.5 = 2, 2 bin里是4 * 0.5 = 2.
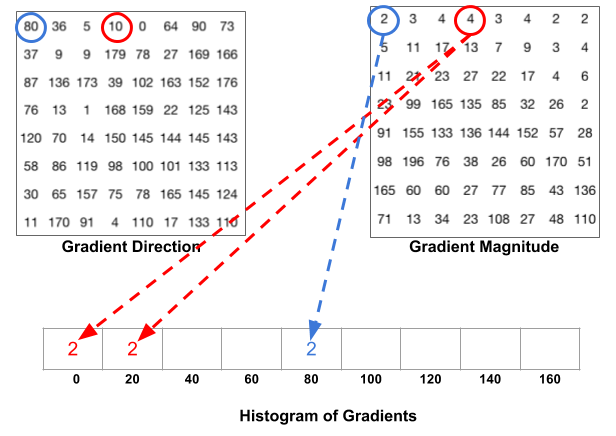
- 遇到边界的(角度在160-180且需要分配的),第二个分配到0
bin里。下图左绿色圈代表角度为165度,165 = 160 * 0.75 + 180 * 0.25,则160
bin里是85 * 0.75 = 63.75, 0
bin(本来应该是180bin但没这个bin换成0bin)为85 * 0.25 = 21.25。
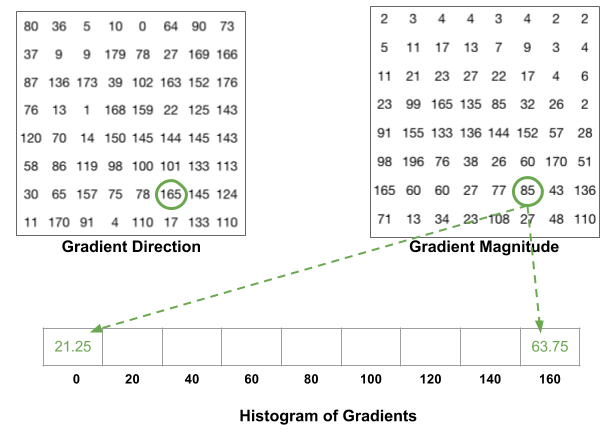
- 先根据角度算每个格子的占比,下图中左红色圈代表角度为10度,介于0-20度之间,10
= 0 * 0.5 + 20 * 0.5,知道这个占比之后按照占比将右边圈代表梯度大小,则0
bin里是4 * 0.5 = 2, 2 bin里是4 * 0.5 = 2.
- Concatenate histogram entries to form a HoG vector for each
block
P.S. 上图中一个block里有四个cell,一个cell生成9*1的histogram如下图,那么四个cell的histogram直接横向拼接接为36*1的element vector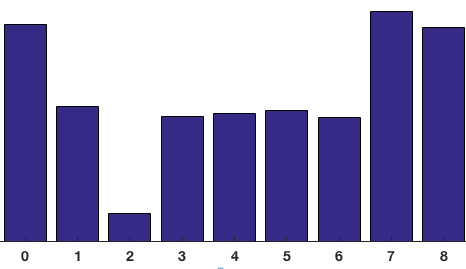
- Normalize vector values by dividing by some function of vector length (单个元素除以全部元素平方和)
COMP3056 Computer Vision 1 -- Image Regions and Patches
https://jerry20000730.github.io/wiki/Lecture Note/COMP3065 Computer Vision/CV2/